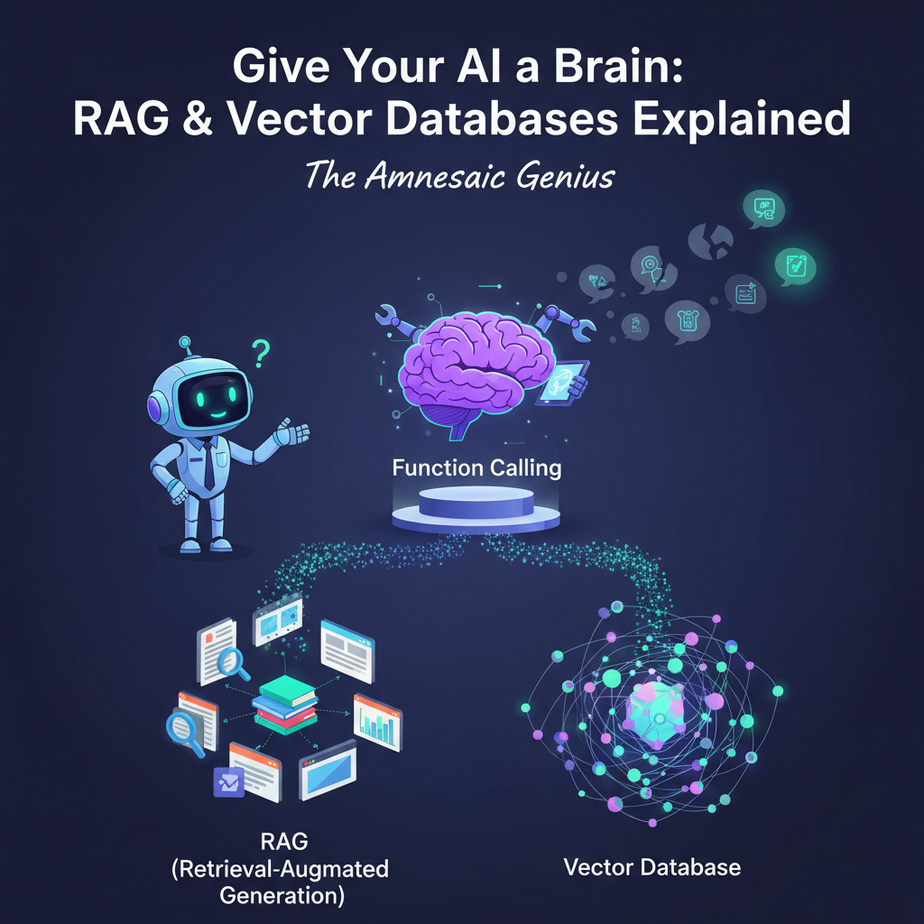
The Amnesiac Genius
Let’s go back to our super-smart intern. Thanks to our last lesson on Function Calling, we performed surgery and gave the brain hands. Now, it can use your tools. It can check an order status. It can update the CRM.
You’re feeling pretty good. You ask the intern, “What’s our company policy on international shipping?”
It responds instantly: “Based on my general knowledge, most companies use carriers like FedEx or DHL and require customs forms…”
“No, no,” you interrupt. “What is *OUR* policy? The one from the 50-page PDF our COO sent out last week?”
The intern stares blankly. “I was not trained on that specific document. I have no memory of it. I have no memory of our conversation five minutes ago. I am a powerful intellect with the memory of a goldfish that just got bonked on the head.”
This is the final, frustrating wall you hit with AI. It knows everything about the public internet up to its training cut-off date, but it knows absolutely *nothing* about your business, your data, or your private documents. It’s a genius who’s never stepped foot in your office.
Today, we’re fixing that. We’re not just giving it hands; we’re giving it a perfect, searchable, long-term memory. We’re building its second brain.
Why This Matters
This is the technology that lets you build an AI that is genuinely *yours*. It’s the difference between a generic tool and a bespoke expert that understands the unique context of your business.
- Business Impact: Instantly get accurate answers from your internal knowledge base (product docs, employee handbooks, legal contracts, customer support history). Stop wasting time searching for information.
- Replaces: The endless searching through shared drives and wikis. The time spent asking colleagues, “Hey, do you know where I can find…?” The expensive process of manually training new employees on company-specific knowledge.
When you master this, your AI goes from being a clever parrot to a seasoned employee who has read every document your company has ever produced.
What This Tool / Workflow Actually Is
This process is called Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). It sounds intimidating, but the concept is as simple as an open-book test.
You’re not *retraining* the model. That’s slow, expensive, and frankly, a terrible idea. Instead, you’re giving the model the relevant textbook pages just before it has to answer the test question.
Here’s the workflow:
- The Library (Vector Database): First, you take all your documents (PDFs, text files, website data) and feed them into a special kind of database called a **Vector Database**. Think of this as a magic library. Instead of storing words, it stores the *meaning* or *semantic concept* of the text. The librarian here is a genius who organizes books by topic and idea, not just by the alphabet. This allows for incredibly intuitive searching.
- The Question (User Prompt): A user asks a question, like, “How many vacation days do I get?”
- The Search (Retrieval): Your system takes the user’s question and asks the magic librarian (the vector database), “Find me the most relevant passages in our entire library about ‘vacation days’.” The database instantly returns the top few matching chunks of text from your employee handbook.
- The Answer (Augmented Generation): Your system then bundles everything up and goes to the LLM. It says: “Hey, using ONLY the following information I found: [*paste relevant chunks from the handbook here*], please answer this user’s question: ‘How many vacation days do I get?'”
The AI then generates a perfect answer based *only* on the documents you provided. No guessing. No making stuff up. Just facts, retrieved from your private data.
Prerequisites
We’re using a few helper libraries to make this incredibly easy. Don’t be intimidated by the list; it’s just a few install commands.
- An OpenAI Account & API Key: We’ll need this for the ‘brain’ (LLM) and the ‘librarian’ (embeddings model).
- Python 3: You know the drill.
- A Few Python Libraries: We’ll use LangChain to simplify the RAG workflow. Open your terminal and run this one command to get everything you need:
pip install langchain langchain-openai faiss-cpu tiktokenfaiss-cpu is our simple, local vector database. No servers, no signups. It just works.
Step-by-Step Tutorial
Let’s build a RAG system from scratch. We’ll create a tiny knowledge base for a fictional company and then ask it questions.
Step 1: Create Your Knowledge Base
Create a new folder for your project. Inside it, create two text files.
policy_vacation.txt:
Company Vacation Policy:
All full-time employees are entitled to 20 paid vacation days per year.
New employees accrue vacation days monthly. Unused days can be rolled over, up to a maximum of 5 days into the next calendar year.policy_expenses.txt:
Company Expense Policy:
Employees can expense up to $50 per day for meals while traveling on business.
All software subscriptions under $100 per month do not require pre-approval.
Expense reports must be submitted via the company portal within 15 days of purchase.Step 2: The Code to Build the ‘Library’
Now create a Python file named build_memory.py. This script will read our documents, chop them up, and store their meanings in our vector database.
import os
from langchain_community.document_loaders import TextLoader
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.text_splitter import CharacterTextSplitter
from langchain_community.vectorstores import FAISS
# --- CONFIGURATION ---
# Make sure to set your OpenAI API key in your environment variables
# or replace this with your key for this simple example.
# os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY"
# --- 1. LOAD DOCUMENTS ---
# For this example, we'll just load one file. A real system would loop through a directory.
loader = TextLoader("./policy_vacation.txt") # You can add the expense policy too!
documents = loader.load()
print(f"Loaded {len(documents)} document.")
# --- 2. SPLIT THE DOCUMENT INTO CHUNKS ---
text_splitter = CharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=1000, chunk_overlap=0)
texts = text_splitter.split_documents(documents)
print(f"Split document into {len(texts)} chunks.")
# --- 3. CREATE EMBEDDINGS AND STORE IN VECTOR DATABASE (FAISS) ---
# OpenAIEmbeddings turns our text into a list of numbers (a vector) representing its meaning.
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
# FAISS is our vector database. It stores the embeddings and allows for fast similarity searches.
db = FAISS.from_documents(texts, embeddings)
# Save the FAISS index to disk
FAISS.save_local(db, "faiss_index_policies")
print("Vector database created and saved locally as 'faiss_index_policies'.")
Run this script: python build_memory.py. It will create a new folder called faiss_index_policies. This is your AI’s brain. You only need to run this script when your documents change.
Complete Automation Example
Now for the fun part. Let’s create a separate script that *uses* this brain to answer questions. This is our **Internal Helpdesk Bot**.
Create a file named ask_memory.py:
import os
from langchain_openai import OpenAI, OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
from langchain_community.vectorstores import FAISS
# --- CONFIGURATION ---
# os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY"
# --- 1. LOAD THE VECTOR DATABASE FROM DISK ---
print("Loading vector database...")
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
db = FAISS.load_local("faiss_index_policies", embeddings, allow_dangerous_deserialization=True)
# --- 2. SET UP THE RAG CHAIN ---
# This chain does the magic: it retrieves relevant docs first, then sends them to the LLM.
qa_chain = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(
llm=OpenAI(),
chain_type="stuff", # "stuff" means it stuffs all retrieved text into the prompt
retriever=db.as_retriever()
)
# --- 3. ASK QUESTIONS! ---
def ask_question(query):
print(f"\
> You asked: {query}")
result = qa_chain.invoke(query)
print(f"< Bot answers: {result['result']}")
print("Internal Helpdesk Bot is ready. Ask a question.")
ask_question("How many vacation days can I roll over to next year?")
ask_question("What is the meal budget for business travel?") # It won't know this if you only loaded the vacation doc!
ask_question("What is the capital of France?") # It will use its general knowledge for this
Now, run this script: python ask_memory.py.
Look at the results! It answers the vacation question perfectly, using the exact text from your policy file. It correctly states it doesn't know the meal budget (because we didn't load that file). And it can still answer general knowledge questions. You've successfully given your AI a targeted, long-term memory.
Real Business Use Cases
This RAG pattern is one of the most powerful tools in AI automation.
- Customer Support Automation: Ingest your entire help center, product manuals, and past support tickets into a vector DB. Build a chatbot that can answer 90% of customer questions instantly and accurately, with links to the source documents.
- Sales Enablement Bot: Feed it all your product spec sheets, pricing documents, and competitor analysis battle cards. A sales rep in the field can ask their phone, "What are the top 3 differentiators between our product and Competitor X?" and get an instant, factual answer.
- Onboarding New Employees: Create a vector DB from your employee handbook, IT setup guides, and internal process documents. A new hire's 'onboarding buddy' is an AI that can answer questions like "How do I set up my VPN?" or "Who do I talk to about payroll?"
- Financial Document Analysis: An investment firm can load hundreds of quarterly earnings reports (10-K filings) into a vector DB. An analyst can then ask, "Summarize the risk factors mentioned by Apple and Google in their latest reports," saving hours of manual reading.
- Legal Contract Review: A law firm can create a knowledge base of all their past cases and contracts. A lawyer can quickly ask, "Find all contracts that contain a 'force majeure' clause related to pandemics," retrieving examples in seconds instead of days.
Common Mistakes & Gotchas
- Garbage In, Garbage Out: RAG is not magic. If your source documents are out of date, poorly written, or contradictory, your AI's answers will be too. The quality of your knowledge base is paramount.
- Bad Chunking Strategy: How you split your documents matters. If your chunks are too small, they lack context. Too big, and they contain too much noise. You have to experiment to find the right size for your data.
- Forgetting to Update the Index: Your vector database is a snapshot in time. If you update a policy document, you *must* remember to re-run the indexing script to update the AI's memory. This should be an automated process in a real system.
- Ignoring Metadata: A good RAG system also stores the source of each chunk (e.g., `policy_vacation.txt`, page 4). This allows your bot to provide citations, which builds user trust and allows for verification.
How This Fits Into a Bigger Automation System
RAG is the memory, but it works best when connected to the other parts of our AI factory.
- RAG + Function Calling: The Ultimate Agent: This is the dream team. An incoming request first goes to the RAG system. Can it be answered from the knowledge base? If yes, great. If no, the agent can then decide to use a **tool** (function call). Example: "What's the status of my last order?" The agent uses the `getOrderStatus()` tool. "What's your return policy?" The agent uses the RAG system to query the policy document.
- Automated Helpdesk: A new ticket comes into your Zendesk or Jira. A webhook triggers your automation. The RAG system reads the ticket, finds the relevant help article, and posts it as a suggested reply, all before a human even sees the ticket.
- Proactive Sales Outreach: An AI agent scans a news feed (its knowledge base). When it sees an article about a company in your CRM launching a new product, it can use that context (RAG) to draft a congratulatory email (Function Calling) for the sales rep to review and send.
What to Learn Next
This has been a journey. We started with a brain (the LLM). We made it fast (Groq). We gave it hands to act in the world (Function Calling). And today, we gave it a perfect, long-term memory for your private data (RAG).
You now possess the complete toolkit to build a single, powerful AI agent. You have created the smartest, fastest, most knowledgeable intern the world has ever seen.
But what happens when one intern isn't enough?
What if you need a team? An entire workforce of AI agents, each with their own specialty, all working together to solve complex, multi-step business problems? A researcher agent that passes its findings to a writer agent, who then hands a draft to an editor agent for approval?
In our next lesson, we move from building a single worker to becoming the architect of an entire AI-powered organization. Welcome to the world of **Multi-Agent Workflows**. It's time to build the factory floor.
",
"seo_tags": "rag, retrieval-augmented generation, vector database, ai memory, langchain, faiss, openai, python tutorial, business automation, knowledge base",
"suggested_category": "AI Automation Courses